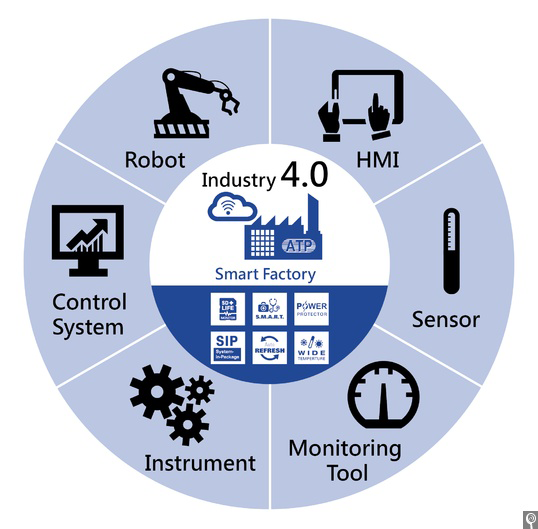
Industry 4.0 introduces what’s called the “smart factory,” in which cyber-physical systems monitor the physical processes of the factory and make decentralized decisions.
The physical systems (machines or Internet of Things) are embeded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and network connectivity which enable these objects to collect and exchange data. Thus, it is able to communicate and cooperate both with each other and with humans in real time via the wireless web.
For a factory or system to be considered Industry 4.0, it must include:
- Inter-operability
Machines, devices, sensors and people that connect and communicate with one another. - Information transparency
The systems create a virtual copy of the physical world through sensor data in order to contextualize information. - Technical assistance
Ability of the systems to support humans in making good decisions and solving problems - Decentralized decision-making
The ability of cyber-physical systems to make simple decisions on their own and become as autonomous as possible.